큐(Queue)란?
컴퓨터의 기본적인 자료구조의 한 가지로, FIFO(First In First Out)구조로 데이터를 저장하는 형식입니다.
스택(Stack)의 LIFO(Last In First Out)와 반대되는 개념
[발단]
혼자 작은 규모로 자동투자 프로그램을 개발하던 도중
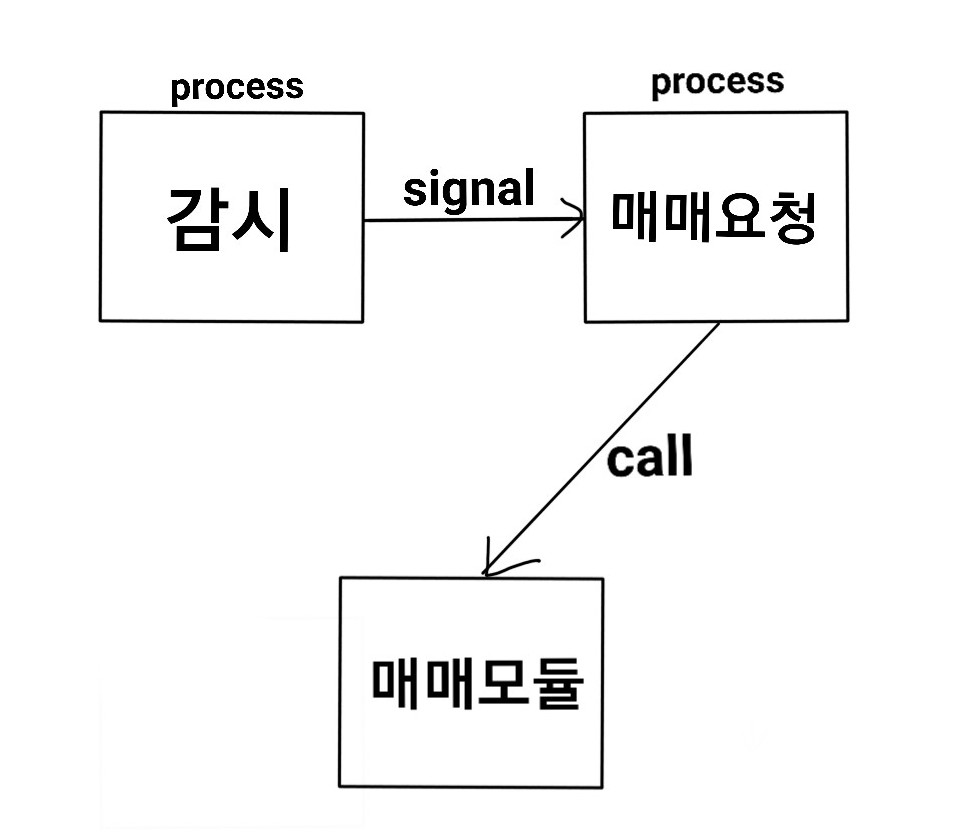
- 실시간 데이터 감시
- 타겟 데이터 포착시 매매 요청
2가지의 기능을 비동기로 구현해야하는 상황이 생겨서 [그림1]의 signal 부분을 Queue를 통해 구현했습니다.
[그림1]
[예시 코드]
Python에서 Queue를 사용하는 간단한 예제입니다.
예제는 3개의 파일로 구성되어 있습니다.
# test_signal.py
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
from test_agent import Agent
from test_trader import Buy, Sell
def run():
queue = Queue()
agent = Agent(queue)
scouter_price = Process(target=agent.scouter_price)
scouter_price.start()
while True:
if not queue.empty():
data = queue.get()
# scouter_price에서 얻은 데이터 활용
if data[0] == 'buy':
Buy(data[1])
if data[0] == 'sell':
Sell(data[1])
if data[0] == -1:
print('종료')
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
# test_agent.py
from time import sleep
class Agent():
def __init__(self, queue):
self.queue = queue
def scouter_price(self):
count = 0
while True:
# 감시 메커니즘 ...
count += 1
sleep(1)
print(f'count: {count}')
if count == 3:
self.queue.put(['buy', count])
if count == 6:
self.queue.put(['sell', count])
if count == 7:
self.queue.put([-1])
break
else:
pass
# test_trader.py
def Buy(data):
# 매수 메커니즘 ...
print(f'{data}로 매수 완료')
def Sell(data):
# 매도 메커니즘 ...
print(f'{data}로 매도 완료')
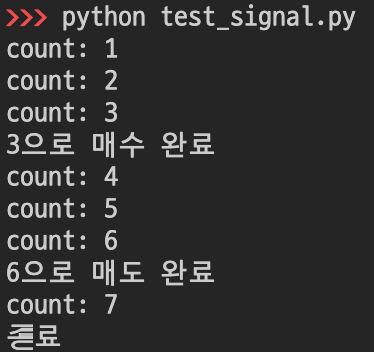
[실행 결과]
실행 카운트 3일 때 3으로 매수 완료, 6일 때 6으로 매도 완료, 7일 때 종료가 출력되고 모든 프로세스가 종료됩니다.